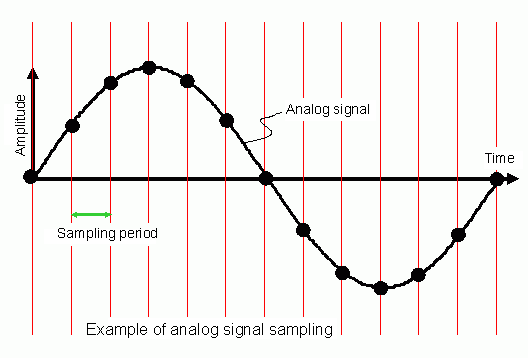
- Sampling
- The process of measuring the value of the analog signal at regular intervals, called samples, and encoding these numerical values in digital form. It is often based on specified quantization levels.
For proper reconstruction of a digital signal a specific sampling rate is necessary. This rate is stipuated by the Nyquist theorem as twice the highest frequency contained in the signal. If this is not observed Aliasing occurs.
- Aliasing
- When the sampling rate of the analog signal falls below Nyquist sampling rate the reproduced digital signal suffers from data loss and is not reproduced faithfully. The resulting digital signal shows static distortion and is a very bad source of reproducing analog signal.

