|
REGISTERS
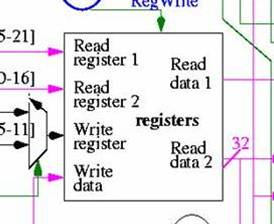
Registers
are specialized locations for information storage. Through the
register component of the processor, information is both stored
and retrieved from specific register locations. This information
is then used for memory address computation, arithemetic computation,
or branch comparisons.
The
address of the information to be read comes in through the two
arrows located on the top left of the component, entitled "read
register 1, read register 2." The register component then
retrieves the data located at these specified locations, and
outputs the data through "read data 1, read data 2."
The write register/write data components are used to store data
in specified registers.
SIGN
EXTENDER
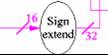
The
sign extender takes a 16 bit input and produces a 32 bit output.
Example:
0000
0000 0000 0010 = 2 ten (16 bit)
0000
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0010 = 2 ten (32 bit)
So
the sign extender increases the size of the input from 16 bits
to 32 bits.
ARITHMETIC
LOGIC UNIT (ALU)
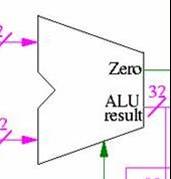
The
arithemtic logic unit, or ALU, performs address calculation,
arithmetic operations, and branch comparisons. This occurs as
a result of the two inputs that come into the ALU from the left
side of the component. Then, based upon the control indicator,
entering from the bottom, one of the forementioned operations
is done upon the incoming data. The result is then output from
the result output line.
Previous/
Next
|